Variable costs are any expenses that change based on how much a company produces and sells, such as labor, utility expenses, commissions, and raw materials. Another important aspect of cost management is optimizing fixed costs. Fixed costs are expenses that do not vary with the level of production or business activities, such as rent, web hosting, and utility bills.
Is Marginal Cost the Same As Variable Cost?

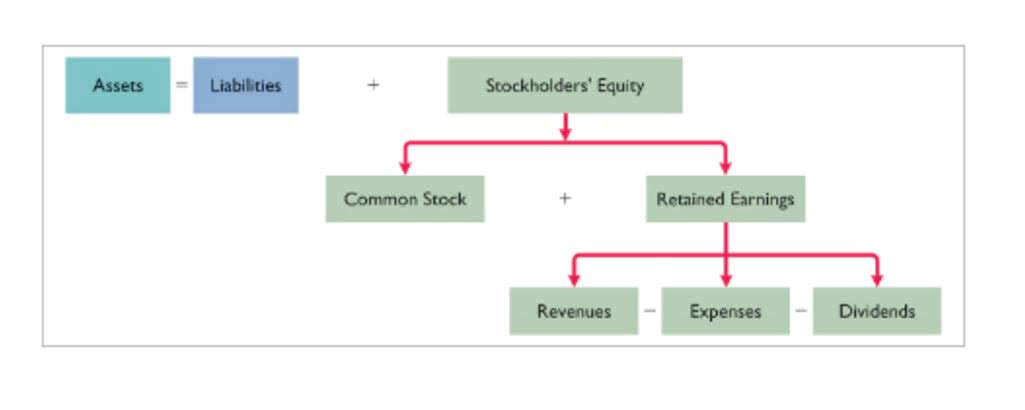
Costs are categorized based on how they respond to changes in production or service levels. Fixed costs do not vary with production volume, while variable costs do. Examining real-life examples of fixed and variable costs can illuminate their impacts on different business models, from manufacturing to services. Your total fixed costs remain the same (because they’re fixed), but your product has doubled, meaning your per-unit cost has halved (so you’ll make more profit on each unit). Lastly, understanding the difference between fixed and variable costs (and how each works) is important to be able to leverage economies of scale as you grow.
The Financial Modeling Certification

Let’s say an employee needs to work overtime as a result of increased sales. Because the overtime wages are due to a rise in sales, they are variable. This would make the employee’s total pay for that pay period (overtime and regular) a mixed cost. Some expenses might have aspects of both fixed and variable costs. This kind of expense is known as a mixed, semi-variable, or semi-fixed cost.
Corporate and Business Entity Forms
These employees will Record Keeping for Small Business receive the same amount of compensation regardless of the number of units produced. For others who are tied to an hourly job, putting in more direct labor hours results in a higher paycheck. Along the manufacturing process, there are specific items that are usually variable costs. For the examples of these variable costs below, consider the manufacturing and distribution processes for a major athletic apparel producer. A firm is only subject to fees if it permits client credit card payments. The credit card fees, which represent a proportion of sales, should be regarded as a variable instead of a monthly fixed cost.
- Variable costs also vary by industry, so it’s important for anyone analyzing companies to make comparisons between those that are in the same industry.
- A variable cost is any business expense that increases or decreases in relation to the company’s revenue, production output, or sales volume.
- Fixed costs are a significant factor in determining your break-even point—the sales level at which your total revenue equals total costs.
- Since they are changing continuously and the amount you spend on them differs from month to month, variable expenditures are harder to monitor and control.
- As an example, you would still have to pay rent and insurance, which would be considered fixed costs.
- You then multiply this by the total number of units produced to calculate your total variable costs for the production of that particular product.
Get Help Making Smarter Decisions with Cost Insights
More workers would be required to produce more goods or deliver more services; hence, some labor might be considered a variable cost. Businesses can use financial data to analyze their cost structures and make informed decisions. Financial data APIs provide real-time insights into costs, helping businesses optimize their pricing, budgeting, and profitability. When sitting down to create a budget, most people start by listing their fixed costs as well as any essential living expenses. This process may include budgeting money for groceries, childcare costs and health insurance coverage.
- For example, a company might buy machinery for a manufacturing assembly line that is expensed over time using depreciation.
- The current variable cost will be higher than before; the average variable cost will remain something in between.
- While both types of expenses can be recurring, fixed costs are more predictable because you pay the same amount – or close to the same amount – every time you make a payment.
- These might include recurring expenses, like your car insurance bill or a mortgage payment.
That is, your fixed costs are the same to produce 100 units fixed vs variable costs as they are to produce 200 units, but your revenue doubles when you sell 200 units. On the other hand, variable costs fluctuate based on your sales activity. One of those cost profiles is a variable cost that only increases if the quantity of output also increases.
- To get the monthly expenditures, divide the yearly expenses by 12.
- For example, the cost of materials that go into producing the widgets will rise as the number of widgets produced increases.
- Understanding the difference between fixed and variable costs is critical for individuals and businesses alike.
- If revenue slows, businesses can immediately reduce these costs to conserve cash.
- Not sure where to start or which accounting service fits your needs?
- For example, if raw material costs increase unexpectedly, your profit margins might shrink unless you increase your price.
The raw materials needed to make each product, selling commissions for every sale, or shipping costs per unit are a few examples of variable costs. Variable costs can be calculated by multiplying the quantity of output by the variable cost per unit of output. So, suppose company ABC produces ceramic mugs for a cost of $2 a mug. If the company produces 500 units, its variable cost will be $1,000. However, if the company does not produce any units, it will not have any variable cost for producing the mugs. Similarly, if the company CARES Act produces 1000 units, the cost will rise to $2,000.
Typically fixed overhead costs are stable and should not change from the budgeted amounts allocated for those costs. However, if sales increase well beyond what a company budgeted for, fixed overhead costs could increase as employees are added, and new managers and administrative staff are hired. Generally, fixed costs will significantly influence an equity’s overall profitability.
How to Reduce Fixed Costs
Examples of fixed costs are rent, employee salaries, insurance, and office supplies. A company must still pay its rent for the space it occupies to run its business operations irrespective of the volume of products manufactured and sold. You’ll need to recruit additional labor to increase your production levels, even though employee salaries are largely consistent and may be a fixed cost.